Remember when generative AI took the world by storm, and everyone was testing the power of artificial intelligence to do some of human beings’ most creative work? As you might imagine, that was not the end of AI innovation – not in the slightest. Now, the conversation has shifted to a new kind of artificial intelligence: agentic AI.
So, what is agentic AI, and how could it impact business and productivity? This article is intended to answer these questions and highlight how companies—including our own—are already using it.
What Is Agentic AI?
Agentic AI refers to artificial intelligence systems capable of autonomous decision-making and action-taking without requiring continuous human oversight. Unlike traditional AI, which responds to commands or queries, agentic AI actively seeks solutions or executes tasks in real-world contexts. It won’t think creatively – it won’t suddenly decide to take over the world, for example. Instead, it will do exactly what you ask, but without having to spell it out every step of the way.
To do this, this technology separates every task in a workflow and creates designated AI “agents” (hence the name agentic AI) to complete each task. Think of it like this: At an automotive plant, the process of building a car is broken down into individual jobs. The plant hires people to do those jobs, and together, they turn a pile of disparate parts into something you can drive.
Agentic AI works the same way – only automated. And it has the potential to be particularly useful in the automation of complex processes like supply chain optimization, customer service automation, personalized education pathways, software development, dynamic resource allocation in cloud computing and more.
What Are its Defining Features?
First, agentic AI is autonomous, operating independently within defined constraints. Essentially, you give it the rules to follow, and it makes decisions that abide by these rules.
Agentic AI also understands and adapts to its environment or circumstances by analyzing input data and leveraging pre-programmed feedback mechanisms to optimize its workflows. And it has remarkable strengths when it comes to working toward and achieving goals: It acts with purpose and evaluates progress, and it has the ability to improve performance through feedback loops.
How is it Different From Generative AI?
| Generative AI | Agentic AI | |
| Core focus | Designed to create outputs (think: words, images, music) | Goes beyond generating outputs to executing actions, managing tasks, and making decisions autonomously |
| Input/output model | Relies on specific prompts to generate outputs | Interacts with systems, data streams, or real-world environments and makes decisions autonomously based on real-time or contextual inputs |
| Ecosystem integration | Often one component of a solution | Integrates multiple AI capabilities (e.g., generative, analytical, predictive) to operate as a holistic system |
| Use case evolution | Focused on content creation, summarization, and ideation | Automates workflows, performs autonomous monitoring and resolves multistep problems |
What Are Some Real-world Examples?
Perhaps the most well-known example of agentic AI in action is Tesla’s autopilot and Full Self-Driving (FSD) technology. While not fully autonomous, these systems automate many aspects of driving through a complex network of workflows, such as monitoring speed, location, and surrounding objects. Each of these tasks relies on AI-driven processes that work together to assist the driver and enable semi-autonomous operation.
Automating the process of driving requires a highly complex network of workflows to complete all the requisite tasks: The system must monitor the vehicle’s speed and location. It must monitor the objects and vehicles surrounding it. It must understand when it needs to slow down, speed up and stop. Each of these jobs can be broken down into a series of tasks that an agent can automate. Then, these workflows are layered on top of each other to create the final outcome: a car that drives autonomously.
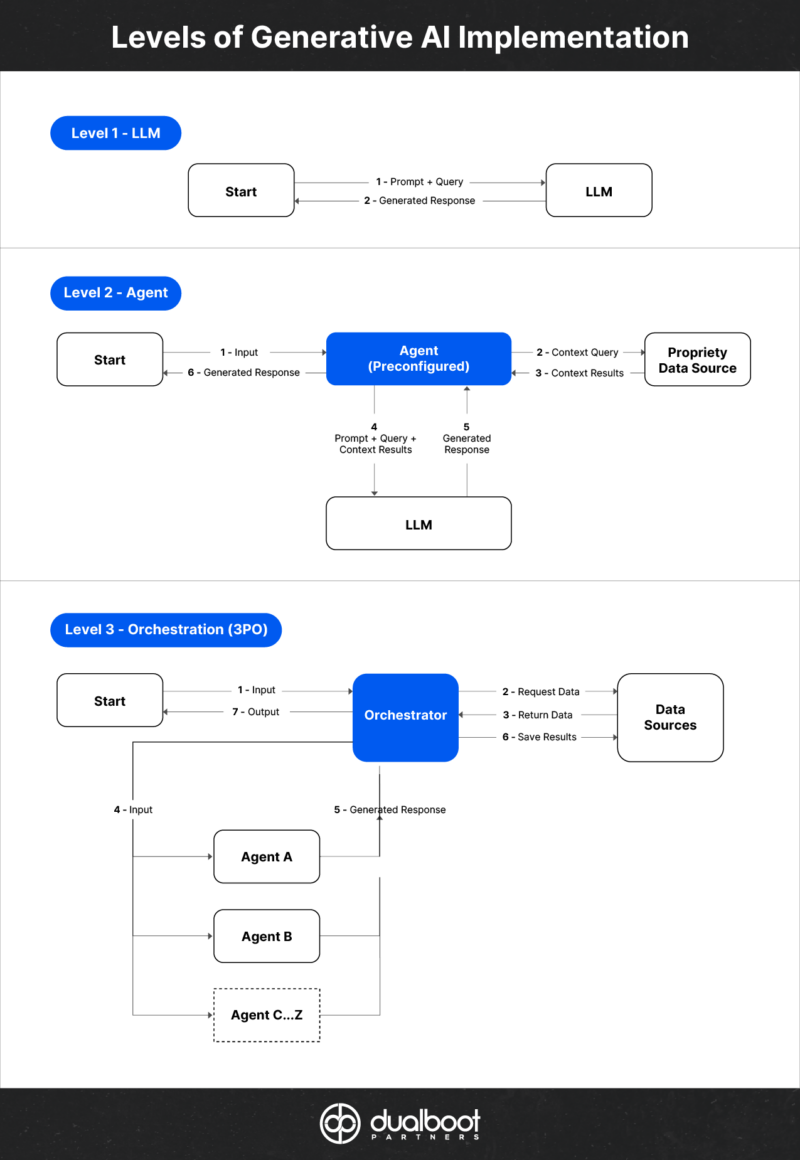
Another example is 3PO, the AI-powered tool we built to modernize legacy software. 3PO leverages a series of specialized agents that autonomously complete distinct tasks within designated workflows. For example, agents analyze existing code bases, identify functionality, assess quality, generate recommendations, and create documentation. Together, these agents achieve the larger goal of extracting core requirements from an existing software application and passing them to additional agents that rewrite the application in a modern technical stack. This layered, autonomous approach demonstrates agentic AI in action.
What’s Coming Next for Agentic AI?
We anticipate that much of the next five years will involve building agentic AI systems for our clients, focusing on automating complex workflows to achieve greater efficiency, accuracy, and speed. Industries such as healthcare, logistics, finance, and manufacturing are particularly well-positioned to benefit from agentic AI. While the potential to redefine automation and innovation is immense, challenges like ensuring data integrity, ethical deployment, and scalability will require thoughtful navigation.
As Bernard Marr highlights in his recent Forbes article, agentic AI represents a paradigm shift in how systems interact, predict, and act autonomously. Marr emphasizes both the transformative potential and the need for robust frameworks to address societal and ethical considerations, reinforcing the importance of navigating this evolution responsibly.
At Dualboot Partners, we intend to be on the front lines of this evolution every step of the way, helping our clients harness the power of agentic AI to redefine automation, drive innovation, and achieve lasting business impact.
Want to learn more about how agentic AI could transform your business?
FAQs
What is Agentic AI?
Agentic AI refers to systems that don’t just generate responses—they take action, make decisions, and execute workflows autonomously within defined constraints. These agents can plan, learn, and adapt rather than waiting for step-by-step instructions.
What the difference between Agentic AI and Generative AI?
Generative AI focuses on producing content (text, images, code) based on prompts. Agentic AI goes further: it coordinates tasks, reasons about goals, interacts with systems, and drives outcomes—not just outputs.
How does Agentic AI differ from traditional AI?
Traditional AI is largely reactive, handling narrow tasks when prompted. Agentic AI is proactive and goal-oriented, operating continuously, making decisions, and improving through feedback loops.
How to build Agentic AI?
Start by defining a high-value business problem, identify workflows that would benefit from autonomy, set guardrails for decision-making, and ensure the right data sources and evaluation metrics are in place.
For a full step-by-step breakdown, we invite you to read the complete insight on Getting Started with Agentic AI.